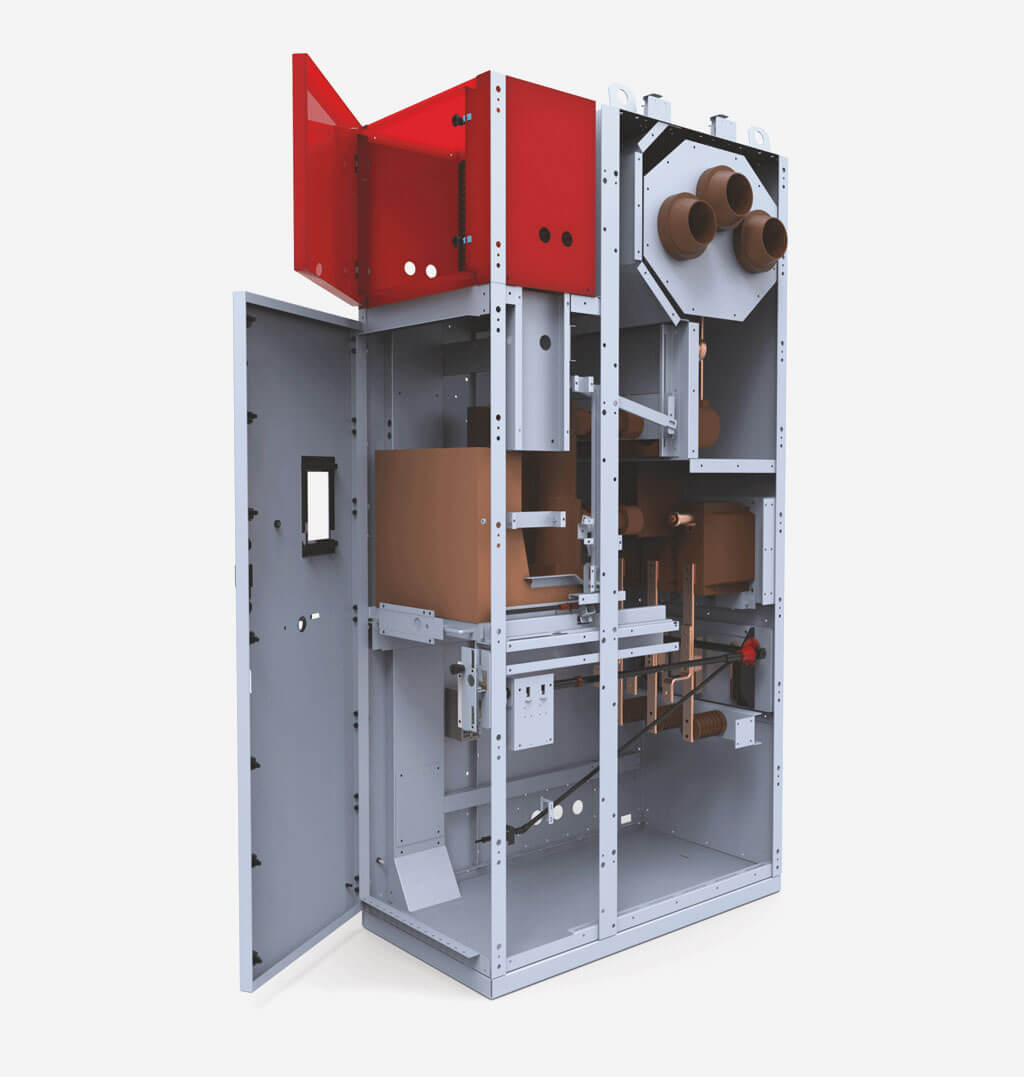
The page presents medium voltage switchgear type RXD:
- air insulated,
- metal enclosed,
- withdrawable or fixed module - depending on equipment,
- with a single busbar system,
- for rated voltages of 12 kV or 36 kV,
- for indoor use.
Highest performance enclosed in an air insulated metal casing. Medium voltage switchgear type RXD works perfectly with up to 36kV, remaining suitable for distribution transformer stations in electric power plants. Thanks to an easy operation, high configurability as well as possibility to expand using additional bays, this ZPUE solution provides great results, while remaining adjustable to electric power industry’s needs. It has been also equipped with withdrawable module that can consist of e.g. contactor, circuit breaker and a set of voltage transformers with fuses.
Designed for rated voltage up to 36kV, the switchgear has been equipped with an additional internal measures to ensure the highest safety of operation. Including a special withdrawable module (allowing maneuvering even when the casing's door is closed), housing resistant to internal arcs and dedicated door-opening interlocks. Thanks to uninterrupted operation even during servicing, we can guarantee the highest efficiency at all times. The correct usage of provided equipment reduces the risk of damage or operator’s injury.
Characteristics of the switchgear
Characteristics
The RXD type switchgear is designed to operate in substations of generation, distribution and industry companies.
It meets the requirements of the (PN-EN) IEC 62271-200 and (PN-EN) IEC 62271-1 standards, provides an IP4X protection degree acc. to (PN-EN) IEC 60529. It is intended for operation in normal conditions, as specified by the (PN-EN) IEC 62271-1 standard.
The switchgear is designed in a manner that ensures that normal operation, inspections and maintenance operations may be performed in a safe manner.
In order to protect against corrosion it uses a frame-less design made of zinc-coated steel sheet, and the doors and side covers of outer bays are powder painted.
Types of Bays
The switchgear may be composed of various functional units:
- incoming/outgoing bays,
- coupler bays,
- metering bays with the possibility of earthing of the main busbars,
- switch disconnector bay,
- transformer bay,
- reactive power compensation bay.
The withdrawable module of the switchgear may be equipped with a circuit breaker, contactor, sectionalizer or a set of fused voltage transformers.
It may be placed in the positions of: service, test/disconnection and separation.
Advantages
- air insulated,
- design constructed with zinc-coated, riveted steel sheets, without welding,
- loss of service continuity - LSC2 for 12 kV and LSC1 for 36 kV,
- version with main busbars in a separate compartment with PM class partitions - for 12 kV,
- high operational safety,
- IAC AFLR internal arc classification,
- interlocks and protections against performing incorrect switching operations,
- wall-standing or free-standing versions, access from the front of the cubicle,
- wide range of devices and bays types,
- possibility of expanding the switchgear with additional bays,
- ease of operation.
The switchgear ensures high operational safety through:
- internal arc resistance of the switchgear enclosure,
- interlocks between switching operations and opening of doors,
- racking in and out the withdrawable module with doors closed,
- the possibility of visual control of switching operations through inspection windows,
- bay voltage indication system.
Basic technical data
Compliance with standards:
The RXD type switchgear meets the requirements of the following standards:
- (PN-EN) IEC 62271-1 - “High-voltage switchgear and controlgear. Common specifications”,
- (PN-EN) IEC 62271-200 - “High-voltage switchgear and controlgear. AC metal-enclosed switchgear and controlgear for rated voltages above 1 kV and up to and including 52 kV”,
The switchgear is certified by appropriate accredited bodies.
| Electrical data: | |||
| Rated voltage | [kV] | 12 | 36 |
| Main busbars and incoming feeder rated continuous current | [A] | 630-1250 | 630 |
| Rated power-frequency withstand voltage | [kV] | 28 | 85 (5min) / 95 (1min) / 120 (5min) |
| Rated lightning impulse withstand voltage | [kV] | 75 | 190/220 |
| Rated frequency | [Hz] | 50 | |
| Rated short-time withstand current | [kA] | up to 25/1s | up to 25/1s |
| Rated peak withstand current | [kA] | up to 63 | up to 63 |
| Withstand for internal arcing fault | [kA] | up to 25/1s | up to 20/1s |
| Protection degree | up to IP4X | ||
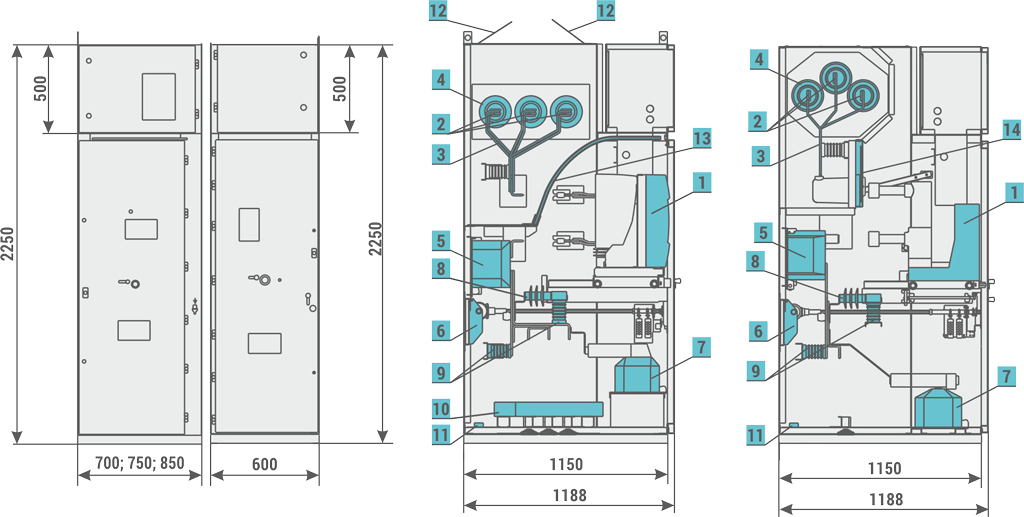
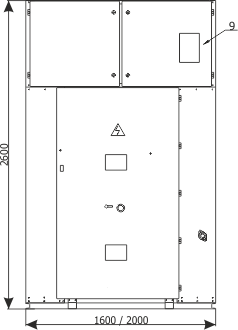
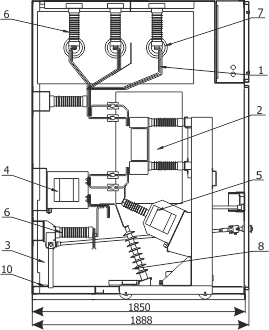
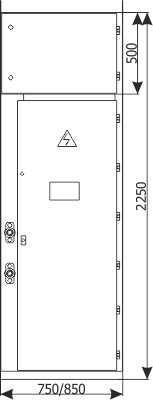
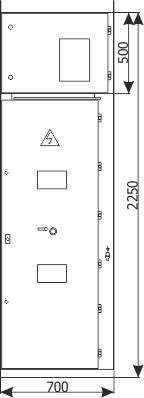
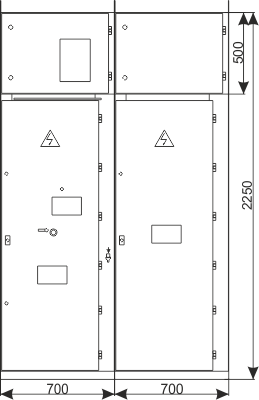
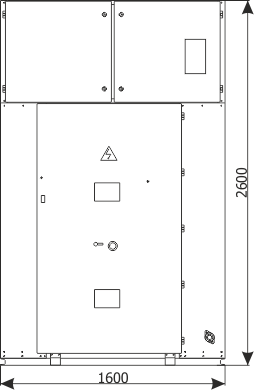
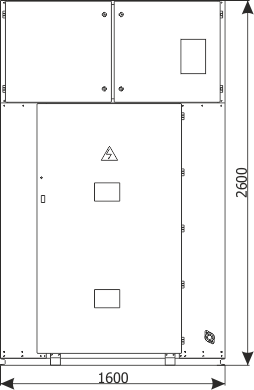
| Cubicle height | [mm] | 2250 | 2600 |
| Cubicle width | [mm] | 600/700/750/900 | 1600/2000 |
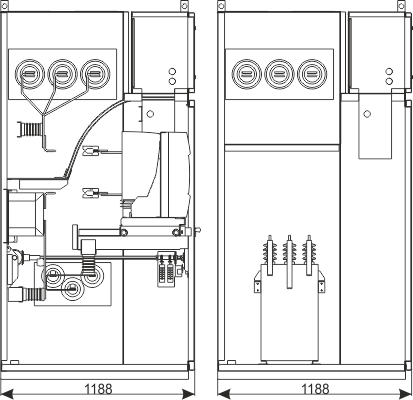
| Cubicle depth | [mm] | 1188 | 1888 |
| Compliance with standards | (PN-EN) IEC 62271-200; (PN-EN) IEC 62271-1 | ||
| Service conditions: | |
| Ambient temperature | Relative humidity of air |
|
- peak short-time+40oC
|
- highest day average95%
|
|
- highest day average+35oC
|
- highest month average90%
|
|
- highest day average vapour pressure2,2kPa
|
|
|
- lowest long-term -5oC
|
- highest month average vapour pressure1,8kPa
|
| Atmosphere at the place of installation |
no significant soiling with salt, vapour, dust, smoke,
flammable or corrosive gasses and lack of icing, frosting and dewing |
| Installation altitude |
up to 1000 m a.s.l.1)
|
| Vibrations |
vibrations caused by external factors
or earthquakes negligible |
Note:
- If the switchgear installation height is higher than 1000 m. a.s.l the switchgear insulation level should be corrected in accordance with the standard.
Switchgear design
Switchgear design
Design
- The switchgear cubicle is constructed of bent steel sheets, riveted together. Walls and partitions create a self-supporting structure. Zinc-coated sheet is used for the construction of cubicles.
- High-strength round-head steel rivets were used as fasteners.
- Additionally, two-part side covers made of painted sheet are bolted to the external walls of the outer bays of the switchgear.
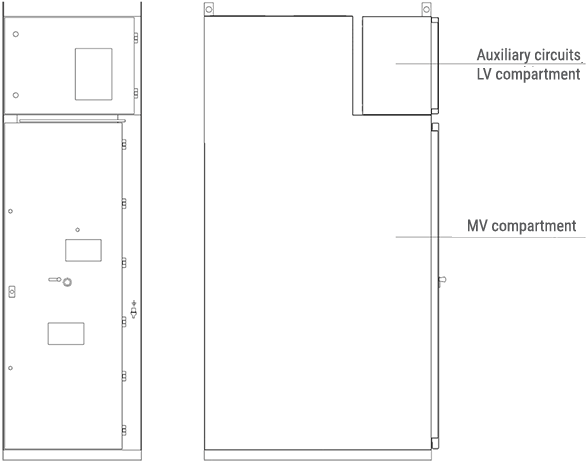
- An auxiliary circuits compartment is placed on top of the cabinet.
- Each cubicle is fully separated from the adjacent cabinets, which prevents damage spreading to adjacent cubicles in case of an electric arc.
- Main busbars are located at the top of the cabinet. The busbars pass between the cabinets through gland plates made of non-magnetic material and equipped with bushings, which are support elements for the main busbars. Outgoing busbars branch off the main busbars.
- The main busbars area can be isolated during servicing by inserting an insulating plate into guide-rails through a slot located above the door (there is also an option of construction of a switchgear with a separate main busbar compartment).
- The cubicle doors may be opened in an interlock-controlled mode.
- The main device may be fixed or as a withdrawable module. The withdrawable module in the operating and test/disconnection positions is located inside the cabinet, behind closed doors. After the doors are opened, it is possible to rack it out to the separation position.
- Mechanical indicators of the circuit breaker position and drive charging state are visible through the inspection window in the switchgear doors.
- In accordance with the LSC (Loss of Service Continuity) classification, the RXD switchgear meets the criteria of LSC2 class (for 12 kV) and LSC1 for 36 kV.
- Connections for cables or busbars are located in the lower zone of the cabinet. It also contains current transformers, fast earthing switch (RXD 12 kV) and depending on operational needs, optionally: voltage transformers, earth fault transformersand surge arresters.
- The earthing switch status is indicated by a position indicator.
- The cubicle bottom is closed by a split floor cover, which also acts as a cable gland plate. Openings in the plate are covered with rubber cable glands.
- Cable clamp supports and earth fault transformer supports are installed on folds of the bottom plate.
The cubicle doors are made of painted sheet. Doors use hinges and bolts which can stand up to explosion-type loads.
The hinges allow opening the doors by approximately 135º.
The doors were reinforced by appropriately shaped and welded reinforcing profiles.
The doors are equipped with an inspection window used for visual control of the position of the withdrawable module and switching operations.
The design of the doors allows the mechanical opening of the circuit breaker in service position with the doors closed.
Safety flaps
The cabinet has in its top part blow-out openings, closed with flaps. Their task is to discharge any pressure created inside the cabinet as a result of an arc fault.
A sudden increase of pressure inside the switchgear cabinet breaks the plastic bolts and opens the flaps, which may activate limit switches installed at the roof of the switchgear. Limit switches activated by the flaps being opened send an impulse which trips the incoming feeder circuit breaker. This allows limiting the effects of an arc fault generated inside the cabinet.
The withdrawable module is a unit composed of a racking system, and depending on the bay function, respectively: circuit breaker, contactor, set of fused voltage transformers, or a sectionalizer. The racking system performs the mechanical connection of the withdrawable module with the switchgear bay. It's stationary part is connected with the bay by interlocking on both sides in guide rail cutouts.
The moving part of the racking system is shifted between the service position and the test/disconnection position using a drive screw operated manually with a crank, or with an electric drive, while the doors are closed. The service and test/disconnection position is signalled by position indicators, after the module reaches an appropriate position.
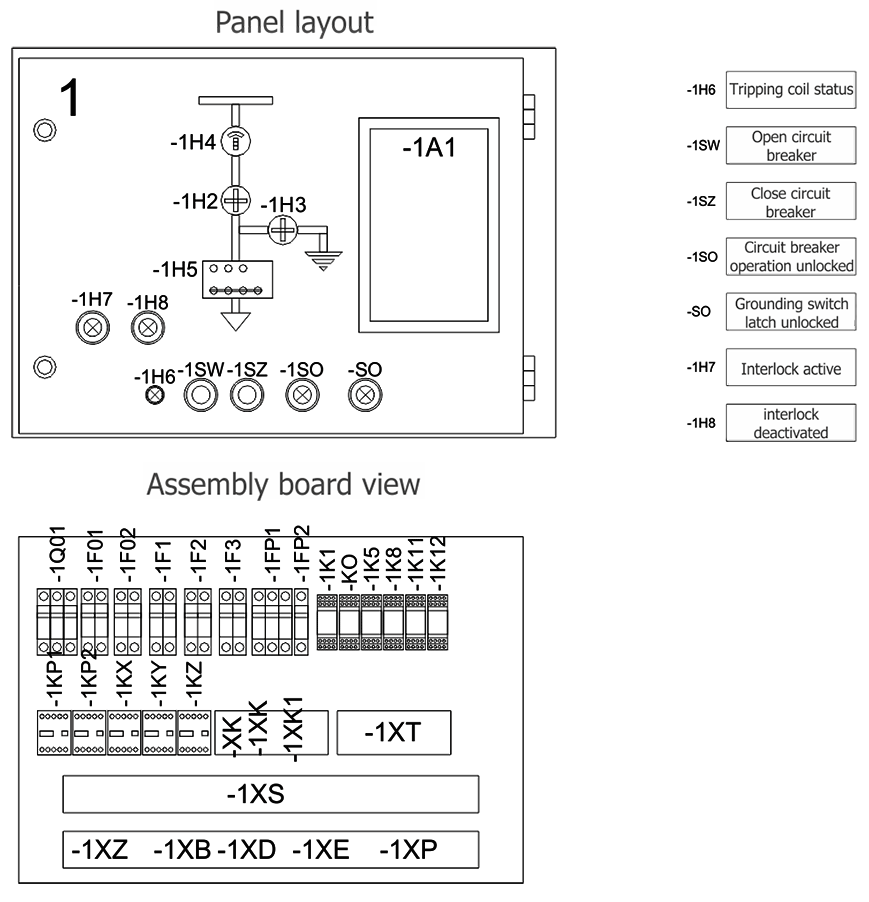
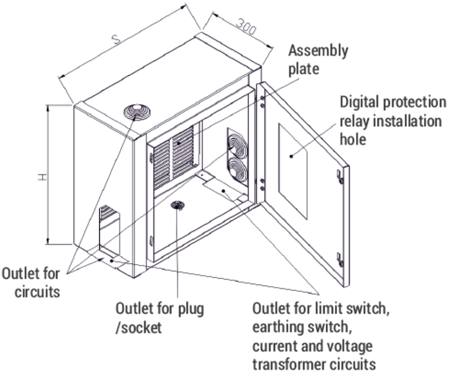
The auxiliary circuits compartment (low voltage compartment) is constructed in the form of a control cubicle and is completely separated from the high voltage zone of the switchgear. The cubicle has its own metal enclosure and may be prefabricated independently of the high voltage part of the switchgear.
The cubicle is intended for the installation of: protection relays and IEDs, instrumentation & control devices and automation system elements.
It is installed on the roof of the switchgear. In its bottom, top and side walls a series of openings are made for lead and cable glands and cable trays.
These openings are covered by plates, in which holes can be made according to design needs. An assembly plate fixed to the rear wall of the LV cubicle was designed for the installation of devices. The devices may be also fixed on the side walls.
On arrangement with the manufacturer, the cubicle design may be adapted to individual needs of the customer and of the design.
Busbars
Main busbars
A single, three-phase current circuit is used as a main busbar in the switchgear, located in the top, back part of the cabinet.
Copper flat bars with rounded edges were used, with cross-sections selected in accordance with the rated current of the switchgear.
The main busbars are supported by distribution busbars and on bushings installed in the side partitions.
Distribution busbars
Distribution busbars are made flat bars with rounded edges, with cross-sections selected in accordance with the rated current of the switchgear.
Insulating elements
The switchgear used epoxy resin insulators. These are post insulators used to support busbars and bushings used to pass the main busbars between the switchgear bays, installed in the gland plates of the bay side walls.
Protective earthing
A earthing conductor is placed in every cabinet, in the form of a copper busbar with a cross-section of 40x5 mm, placed at the bottom, in the rear of the cabinet. These busbars are bridged between the cabinets, creating an earthing conduit. This conduit is terminated with terminals on the left and right side of the switchgear, used to connect it to the facility's earthing system.
Cable connections
The cabinet connection is adapted for entry of single- or multi-core MV cables.
System od interlocks and protections
The switchgear may be equipped with a series of standard and, on arrangement with the manufacturer, other additional mechanical and electrical interlocks which improve operational safety.
Mechanical interlocks:
- prevent racking the withdrawable module in or out of the service position when the circuit breaker is closed,
- allow the closing of the circuit breaker only in the service and test/disconnection positions,
- allow the closing of the earthing switch only in the test/disconnection or separation position of the withdrawable module,
- prevent racking the withdrawable module from the test/disconnection position to the service position if the earthing switch is closed,
- allow changing the position of withdrawable module only when it is locked in a bay,
- prevent opening the bay door if the earthing switch is open (does not apply to RXD36),
- prevent racking the withdrawable module from the test/disconnection position to the separation position until the circuit breaker control circuits supply plug is set to the separation position (optional),
- a servicing truck for the transporting of withdrawable modules may be equipped with a secure bay coupling mechanism, which prevents changing the position of the racking truck even when its wheels are unlocked (optional),
- a servicing truck for the transporting of withdrawable modules may be constructed in a way that allows moving the withdrawable module from the truck to the bay only after mechanical coupling of the truck with the bay (optional),
- a servicing truck for the transporting of withdrawable modules may be constructed in a way that allows uncoupling the truck from the bay only after the withdrawable module is locked in the bay or in the truck (optional),
- allow locking the drive of moving partitions which cover the fixed contacts.
On arrangement with the manufacturer it is possible to use additional key and padlock interlocks.
Electrical interlocks:
- prevent closing the circuit breaker if its auxiliary circuits are not powered; only mechanical opening of the circuit breaker is possible (optional),
- prevent racking the withdrawable module to the service position without power supply to the control circuits (optional),
- prevent access to the earthing switch drive when closing of the earthing switch requires additional conditions (for example, main busbar earthing switch can be closed only when the withdrawable modules in the particular section are in the test/disconnection position),
- prevent access to the withdrawable module drive when racking the module requires additional conditions (optional).
Interlocks, with the exception of standard interlocks, are always designed to fit to a particular project.
On arrangement with the switchgear's manufacturer, it is possible to install additional interlocks, which operate based on limit switches and electromagnetic locks.
The door design allows them to be unlocked and the withdrawable module drive to be accessed when needed (this special activity may be unsafe).
Switchgear equipment
Switching devices
The switchgear may be equipped as with VB-4 (ZPUE), SION (Siemens), VD4 (ABB), HVX (Schneider) vacuum circuit breakers; HD4 (ABB) gas insulated circuit breakers; 3TM (Siemens), ConVac (ABB) contactors, and also Rollarc (Schneider Electric) on arrangement. Other devices may be used on arrangement with the switchgear manufacturer. A fast earthing switch with an impulse drive is used (with the exception of RXD 36).
Metering instrumentation
Instrument transformers by different manufacturers are used for metering purposes.
Bay voltage indication utilizes capacitive insulators or voltage transformers with voltage dividers and voltage indicator type SN (ZPUE).
Protection devices
The switchgear can be equipped with low voltage devices by any manufacturer, according to the individual needs of the customer. It is also possible to install any digital protection relay or IED.
An internal arc protection system can be installed in the switchgear.
The systems sense the internal arc by detecting the flash and an addtional voltage or current criteria inside the protected switchgear.
When these two events occur simultaneously, the system is activated and a circuit breaker tripping impulse is sent.
Diagrams of primary and auxiliary circuits, switchgear automation
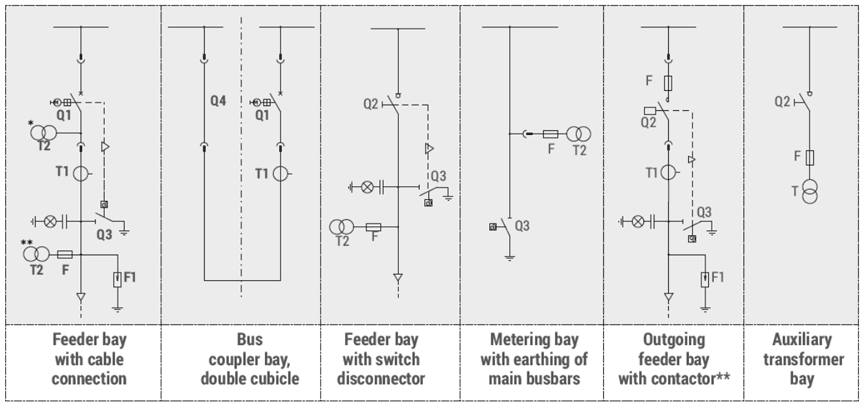
Primary circuits
Structural diagrams of examples of primary circuits are shown on Figure 2 and in data sheets provided herein and on the website. Alternative solutions to the ones presented can be implemented on arrangement with the manufacturer.
Auxiliary circuits
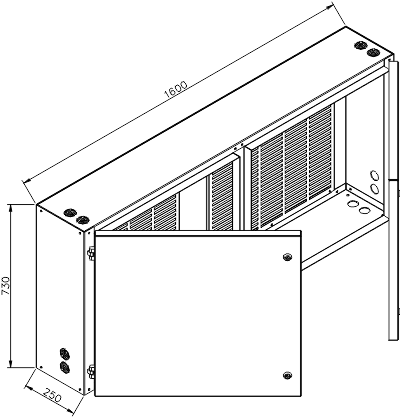
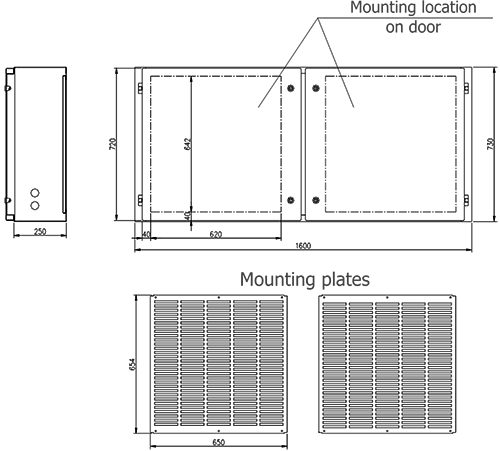
LV auxiliary circuits consist of: protection relays, metering, control, automation and signalling systems. An auxiliary circuits compartment is intended for the devices of these circuits. Dimensions and example arrangement of devices are presented on figures 3
and 4.
Diagrams of example internal and assembly connections for primary and auxiliary devices for a typical switchgear equipment can be obtained by contacting the switchgear manufacturer.
Switchgear automation
The switchgear is designed to operate in SCADA systems. With this goal in mind it is equipped with digital protection relays (with possible digital communication) and automation systems. The switchgear can then operate in master control systems and automated control systems.
Switchgear packaging, transport and installation
Packaging
Three packaging methods are used for RXD type switchgears:
- standard packaging - the switchgear cubicles is placed on a pallet and wrapped with bubble wrap followed by shrink wrap,
- in boxes - switchgear cubicles are packaged as described above and put into boxes,
- maritime transport packaging - switchgear cubicles with inserted moisture absorbing material are placed in barrier plastic sheet bags, which are evacuated. The switchgears protected in this manner are transported respectively on pallets or in boxes.
Transport
Switchgears are transported as single cubicles or as cubicles assembled into transport assemblies. Transport of the switchgear in the room and to the room in which it is to be installed can be done with a crane, forklift, or on rollers.
For crane transport, the cubicles is equipped with transport lugs. The angle of lifting ropes should not exceed 120°. Attaching the lifting ropes directly to the cubicles structure is prohibited.
The placement of the cubicles on a transport pallet enables lifting the switchgear with a forklift.
During the transport and installation of the switchgear cubicles, great care should be taken to not to damage the paintwork and steel sheet enclosures.
Main devices, such as circuit breakers, contactors, and withdrawable modules, and LV devices sensitive to vibrations, are transported separately in the manufacturers' original packages.
Switchgear installation
The manner of switchgear placement and external cable and busbar connections depend on the design of the facility where it will be placed. These connections should be performed according to the instructions established during arrangements with the switchgear manufacturer.
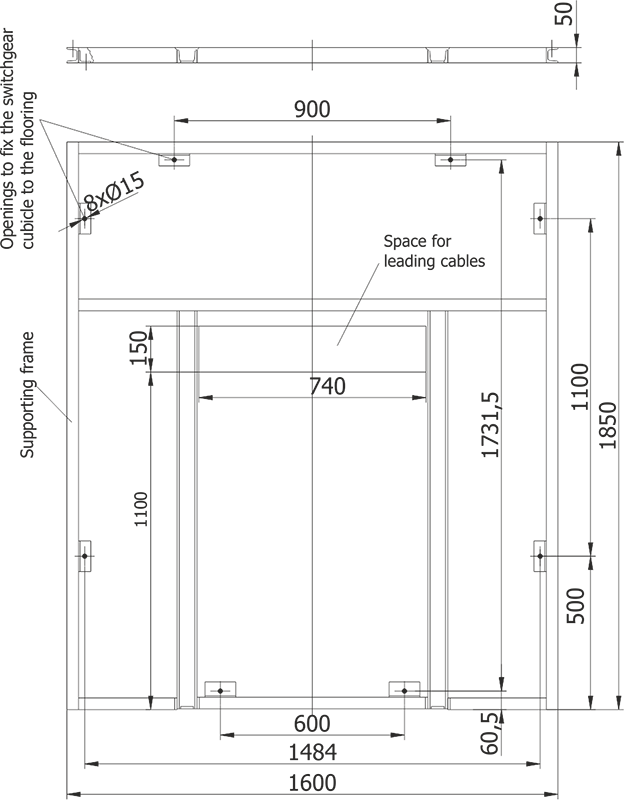
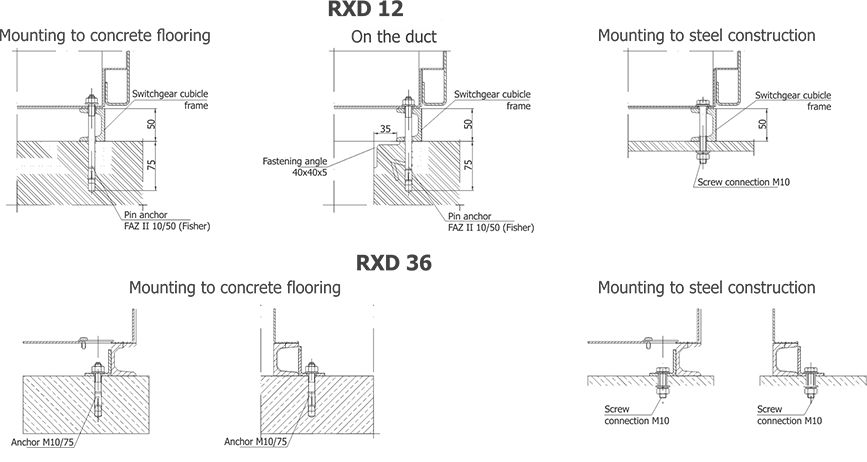
The switchgears can be placed directly on concrete floor, on foundation frame attached to the floor, or on a steel or concrete structure of the facility.
Regardless of the type of foundation, switchgears must be placed horizontally, well levelled and attached to the foundation.
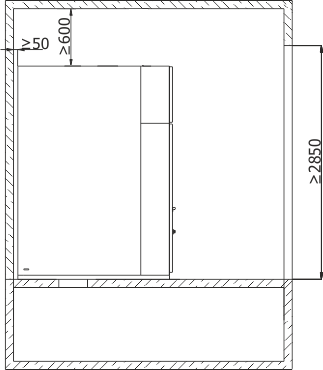
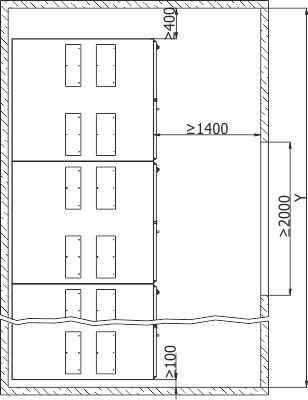
Figures 5 and 6 present the principles of switchgear placement: location of the switchgear in the room, example locations of floor holes for cable entries, switchgear support frame with holes for attaching the switchgear to the foundation.
They should be treated as demonstrations, and their exact location agreed upon when ordering the switchgear. Figure 7 demonstrates methods for attaching the switchgears to the foundation.
Due to the switchgear installation technology it is recommended that the Y dimension of the room be at least 1000 mm higher than the total length of the switchgear.
Recommended minimum distance from closed safety flaps on the switchgear roof to the room ceiling: 600 mm.
Standard equipment delivered with the switchgear
Each switchgear is equipped with:
- fasteners for connecting all the units together,
- withdrawable module racking crank,
- earthing switch drive crank,
- withdrawable module transport cart,
- cabinet key doors.
Documents delivered with the switchgear:
- declaration of conformity,
- switchgear manual,
- operation and maintenance manuals and warranty cards for the used devices,
- as-built documentation for the switchgear,
- warranty card.
Drawings
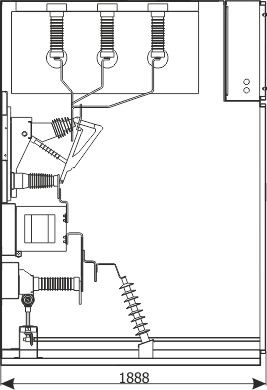
Figure 1a - Example equipment of the RXD 12 bay
- main device: circuit breaker contactor
- main busbars
- outgoing busbars
- bushings
- current transformers
- earthing switch
- voltage transformers
- surge arresters
- capacitive post insulators
- earth fault transformer
- earthing busbar
- safety flaps
- insulating plate
- partition with insulator
Figure 3a - RXD 12 bay auxiliary circuits compartment
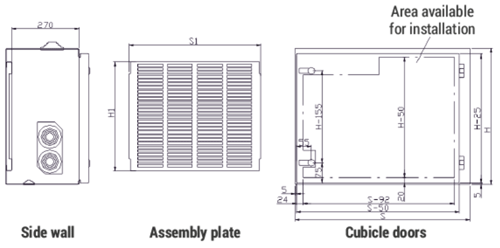
| Dimensions [mm] | ||||
| H | 500 | 500 | 500 | 500 |
| S | 900 | 750 | 700 | 600 |
| H1 | 450 | 450 | 450 | 450 |
| S1 | 820 | 670 | 630 | 520 |
Figure 5a - Placement of the RXD 12 switchgear
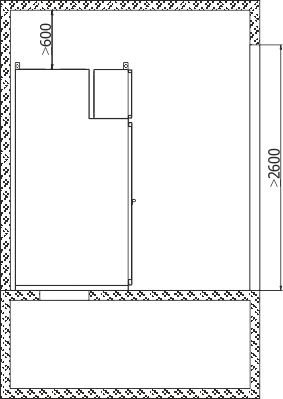
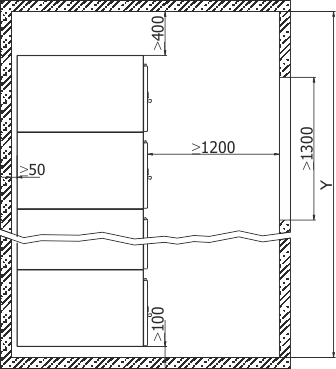
Figure 5b - Placement of the RXD 36 switchgear
Data sheets examples
RXD 12 kV
| RXD 12 kV | ||
| 1. | Sheet 1.1 | Feeder bay with circuit breaker, 12 kV |
| 2. | Sheet 1.2 | Feeder bay with circuit breaker and a separate compartment of main busbars, 12 kV |
| 3. | Sheet 1.4 | Feeder bay with switch disconnector, 12 kV |
| 4. | Sheet 1.6 | Bus coupler bay - cubicle with circuit breaker, 12 kV |
| 5. | Sheet 1.8 | Bus coupler bay - cubicle with sectionalizer, 12 kV |
| 6. | Sheet 1.10 | Metering bay, 12 kV |
| 7. | Sheet 1.11 | Metering bay with a separate compartment of main busbars, 12 kV |
| 8. | Sheet 1.13 | Auxiliary transformer bay - with a transformer up to 40 kVA, 6/0.4 kV |
| 9. | Sheet 1.14 | Reactive power compensation set - with a capacitor bank up to 700 kvar; 6.6 kV |
| * These data sheets are exemplary solutions which can be changed. In case of switchgears with technical parameters and bay configurations different than the ones presented, appropriate data sheets are available directly from the manufacturer or on the www.zpue.com website. |
||
Sheet 1.1 - Feeder bay with circuit breaker, 12 kV
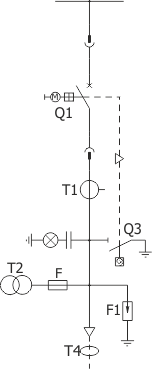
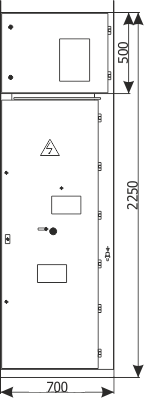
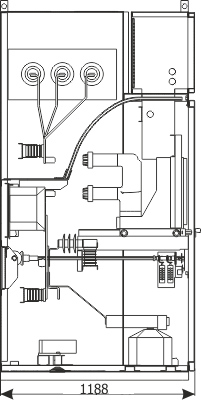
| Parameters: | ||
| Rated voltage | [kV] | 12 |
| Rated power-frequency withstand voltage | [kV] | 28 |
| Rated lightning impulse withstand voltage | [kV] | 75 |
| Rated frequency | [Hz] | 50 |
| Rated continuous current | [A] | 630-1250 |
| Main busbars rated cotinuous current | [A] | 630-1250 |
| Rated short-time withstand current | [kA/1s] | up to 25 |
| Rated peak withstand current | [kA] | up to 65 |
| Withstand for internal arcing fault | [kA/1s] | up to 25 |
| Protection degree | up to IP4X | |
| Equipment: | ||
| Circuit breaker | Q1 | VB-4 (ZPUE); SION (Siemens); VD4/HD4 (ABB); HVX (Schneider Electric) |
| Earthing switch | Q3 | US1 (ZPUE); EK6 (ABB) |
| Current transformer | T1 | various manufacturers |
| Voltage transformer | T2 | various manufacturers |
| Earth fault transformer | T4 | various manufacturers |
| Surge arrester | F1 | various manufacturers |
| Weight | [kg] | 560-700 |
| Note: We allow the possibility of arranging the bay configuration concerning its function and equipment (type/manufacturer) |
||
Sheet 1.2 - Feeder bay with circuit breaker and a separate compartment of main busbars, 12 kV
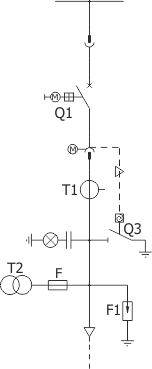
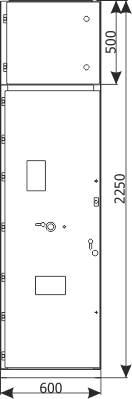
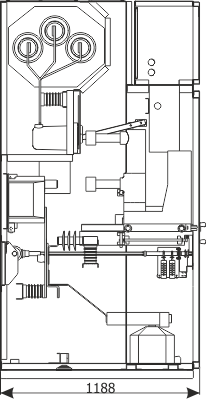
| Parameters: | ||
| Rated voltage | [kV] | 12 |
| Rated power-frequency withstand voltage | [kV] | 28 |
| Rated lightning impulse withstand voltage | [kV] | 75 |
| Rated frequency | [Hz] | 50 |
| Rated continuous current | [A] | 630-1250 |
| Main busbars rated cotinuous current | [A] | 630-1250 |
| Rated short-time withstand current | [kA/1s] | up to 25 |
| Rated peak withstand current | [kA] | up to 63 |
| Withstand for internal arcing fault | [kA/1s] | up to 25 |
| Protection degree | up to IP4X | |
| Equipment: | ||
| Circuit breaker | Q1 | VB-4 (ZPUE); SION (Siemens); VD4/HD4 (ABB); HVX (Schneider) |
| Earthing switch | Q3 | US1 (ZPUE); EK6 (ABB) |
| Current transformer | T1 | various manufacturers |
| Voltage transformer | T2 | various manufacturers |
| Surge arrester | F1 | various manufacturers |
| Weight | [kg] | 650 |
| Note: We allow the possibility of arranging the bay configuration concerning its function and equipment (type/manufacturer) |
||
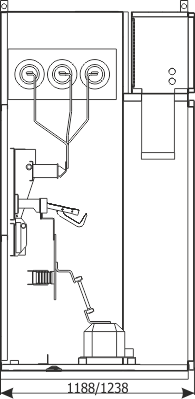
Sheet 1.4 - Feeder bay with switch disconnector, 12 kV
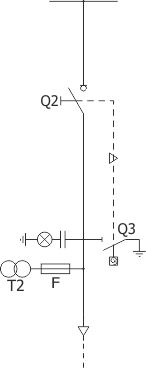
| Parameters: | ||
| Rated voltage | [kV] | 12 |
| Rated power-frequency withstand voltage | [kV] | 28 |
| Rated lightning impulse withstand voltage | [kV] | 75 |
| Rated frequency | [Hz] | 50 |
| Rated continuous current | [A] | 630-1250 |
| Main busbars rated cotinuous current | [A] | 630-1250 |
| Rated short-time withstand current | [kA/1s] | up to 25 |
| Rated peak withstand current | [kA] | up to 63 |
| Withstand for internal arcing fault | [kA/1s] | up to 25 |
| Protection degree | up to IP4X | |
| Equipment: | ||
| Switch disconnector | Q2 | NAL (ABB); OM (ZWAE) |
| Earthing switch | Q3 | fast, with an impulse drive |
| Voltage transformer | T2 | various manufacturers |
| Weight | [kg] | 520-620 |
| Note: We allow the possibility of arranging the bay configuration concerning its function and equipment (type/manufacturer) |
||
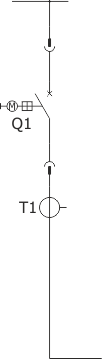
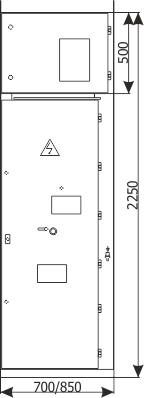
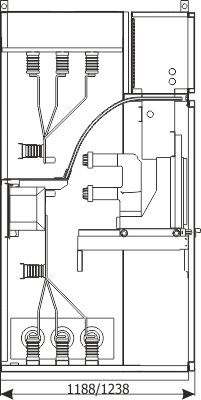
Sheet 1.6 - Bus coupler bay - cubicle with circuit breaker, 12 kV
| Parameters: | ||
| Rated voltage | [kV] | 12 |
| Rated power-frequency withstand voltage | [kV] | 28 |
| Rated lightning impulse withstand voltage | [kV] | 75 |
| Rated frequency | [Hz] | 50 |
| Rated continuous current | [A] | 630-1250 |
| Main busbars rated cotinuous current | [A] | 630-1250 |
| Rated short-time withstand current | [kA/1s] | up to 25 |
| Rated peak withstand current | [kA] | up to 63 |
| Withstand for internal arcing fault | [kA/1s] | up to 25 |
| Protection degree | up to IP4X | |
| Equipment: | ||
| Circuit breaker | Q1 | VB-4 (ZPUE); SION (Siemens); VD4/HD4 (ABB); HVX (Schneider Electric); |
| Current transformer | T1 | various manufacturers |
| Weight | [kg] | 530-630 |
| Note: We allow the possibility of arranging the bay configuration concerning its function and equipment (type/manufacturer) |
||
Sheet 1.8 - Bus coupler bay - cubicle with sectionalizer, 12 kV

| Parameters: | ||
| Rated voltage | [kV] | 12 |
| Rated power-frequency withstand voltage | [kV] | 28 |
| Rated lightning impulse withstand voltage | [kV] | 75 |
| Rated frequency | [Hz] | 50 |
| Rated continuous current | [A] | 630-1250 |
| Main busbars rated cotinuous current | [A] | 630-1250 |
| Rated short-time withstand current | [kA/1s] | up to 25 |
| Rated peak withstand current | [kA] | up to 63 |
| Withstand for internal arcing fault | [kA/1s] | up to 25 |
| Protection degree | up to IP4X | |
| Equipment: | ||
| Sectionalizer | Q4 | made by ZPUE |
| Weight | [kg] | 405-510 |
| Note: We allow the possibility of arranging the bay configuration concerning its function and equipment (type/manufacturer) |
||
Sheet 1.10 - Metering bay, 12 kV
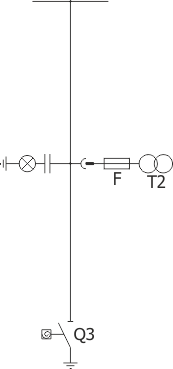
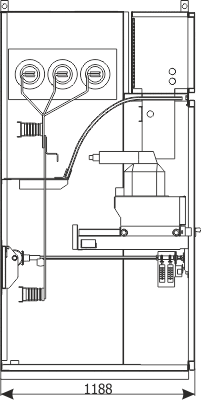
| Parameters: | ||
| Rated voltage | [kV] | 12 |
| Rated power-frequency withstand voltage | [kV] | 28 |
| Rated lightning impulse withstand voltage | [kV] | 75 |
| Rated frequency | [Hz] | 50 |
| Main busbars rated cotinuous current | [A] | 630-1250 |
| Rated short-time withstand current | [kA/1s] | up to 25 |
| Rated peak withstand current | [kA] | up to 63 |
| Withstand for internal arcing fault | [kA/1s] | up to 25 |
| Protection degree | up to IP4X | |
| Equipment: | ||
| Withdrawal module | withdrawable module with voltage transformers | |
| Earthing switch | Q3 | US1 (ZPUE); EK6 (ABB) |
| Voltage transformer | T2 | various manufacturers |
| Weight | [kg] | 440-540 |
| Note: We allow the possibility of arranging the bay configuration concerning its function and equipment (type/manufacturer) |
||
Sheet 1.11 - Metering bay with a separate compartment of main busbars, 12 kV
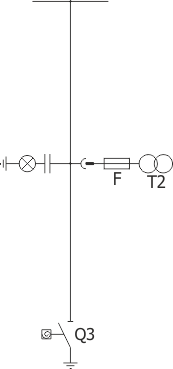
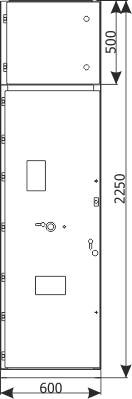
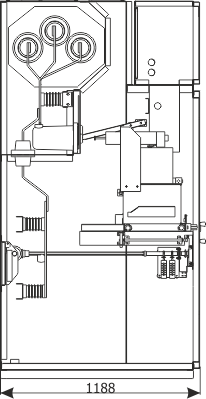
| Parameters: | ||
| Rated voltage | [kV] | 12 |
| Rated power-frequency withstand voltage | [kV] | 28 |
| Rated lightning impulse withstand voltage | [kV] | 75 |
| Rated frequency | [Hz] | 50 |
| Main busbars rated cotinuous current | [A] | 630-1250 |
| Rated short-time withstand current | [kA/1s] | up to 25 |
| Rated peak withstand current | [kA] | up to 63 |
| Withstand for internal arcing fault | [kA/1s] | up to 25 |
| Protection degree | up to IP4X | |
| Equipment: | ||
| Withdrawal module | withdrawable module with voltage transformers | |
| Earthing switch | Q3 | US1 (ZPUE); EK6 (ABB) |
| Voltage transformer | T2 | various manufacturers |
| Weight | [kg] | 470 |
| Note: We allow the possibility of arranging the bay configuration concerning its function and equipment (type/manufacturer) |
||
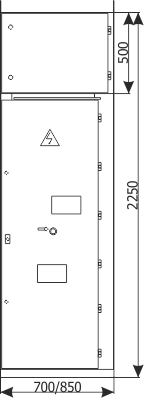
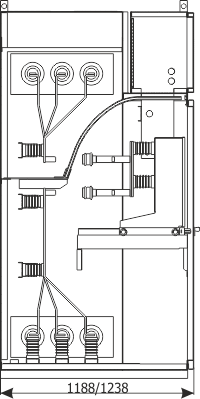
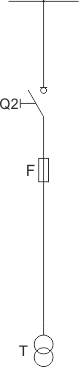
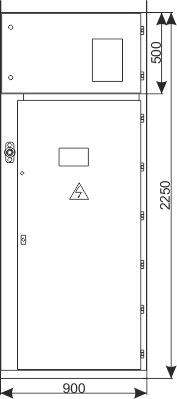
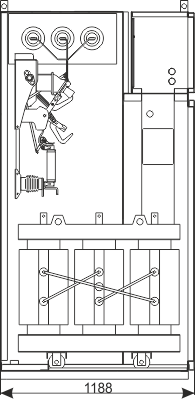
Sheet 1.13 - Auxiliary transformer bay - with a transformer up to 40 kVA, 6/0.4 kV
| Parameters: | ||
| Rated voltage | [kV] | 12 |
| Rated power-frequency withstand voltage | [kV] | 28 |
| Rated lightning impulse withstand voltage | [kV] | 75 |
| Rated frequency | [Hz] | 50 |
| Main busbars rated cotinuous current | [A] | 630-1250 |
| Rated short-time withstand current | [kA/1s] | up to 25 |
| Rated peak withstand current | [kA] | up to 63 |
| Withstand for internal arcing fault | [kA/1s] | up to 25 |
| Protection degree | up to IP4X | |
| Equipment: | ||
| Switch disconnector | Q2 | NALF (ABB); OMB (ZWAE) |
| Transformer | T | up to 40 kVA; 6/0,4 kV |
| Weight | [kg] | 890 |
| Notice: We allow the possibility of arranging the bay configuration concerning its function and equipment (type/manufacturer) |
||
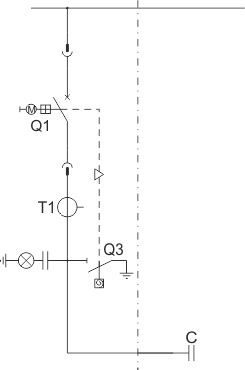
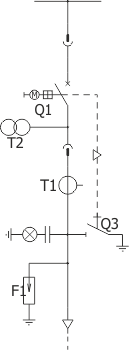
Sheet 1.14 - Reactive power compensation set - with a capacitor bank up to 700 kvar; 6.6 kV
| Parameters: | ||
| Rated voltage | [kV] | 12 |
| Rated power-frequency withstand voltage | [kV] | 28 |
| Rated lightning impulse withstand voltage | [kV] | 75 |
| Rated frequency | [Hz] | 50 |
| Main busbars rated cotinuous current | [A] | 630-1250 |
| Rated short-time withstand current | [kA/1s] | up to 25 |
| Rated peak withstand current | [kA] | up to 63 |
| Withstand for internal arcing fault | [kA/1s] | up to 25 |
| Protection degree | up to IP4X | |
| Equipment: | ||
| Circuit breaker/contactor | Q1 | VB-4 (ZPUE); SION (Siemens); VD4/HD4 (ABB); HVX (Schneider Electric); 3TM (Siemens), ConVac (ABB) |
| Earthing switch | Q3 | US1 (ZPUE); EK6 (ABB) |
| Current transformer | T1 | various manufacturers |
| Capacitor bank | C | up to 700 kvar; 6,6 kV |
| Weight | [kg] | 960 |
| Note: We allow the possibility of arranging the bay configuration concerning its function and equipment (type/manufacturer) |
||
RXD 36 kV
| RXD 36 kV | ||
| 1. | Sheet 2.1 | Feeder bay with circuit breaker |
| 2. | Sheet 2.2 | Feeder bay with switch disconnector |
| 3. | Sheet 2.3 | Bus coupler bay - cubicle with circuit breaker |
| 4. | Sheet 2.4 | Bus coupler bay - cubicle with sectionalizer |
| 5. | Sheet 2.5 | Metering bay |
| 6. | Sheet 2.6 | Auxiliary transformer bay |
| * These data sheets are exemplary solutions which can be changed. In case of switchgears with technical parameters and bay configurations different than the ones presented, appropriate data sheets are available directly from the manufacturer or on the www.zpue.com website. | ||
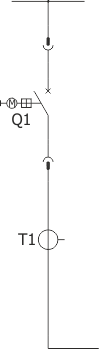
Sheet 2.1 - Feeder bay with circuit breaker
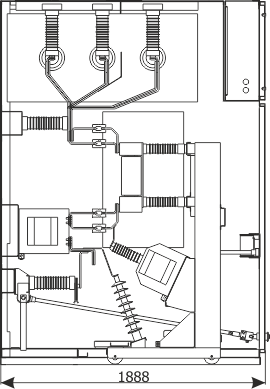
| Parameters: | |||
| Rated voltage | [kV] | 36 | |
| Rated power-frequency withstand voltage | to earth and between phases | [kV] | 85 (5min) / 95 (1min) |
| across the isolating distance | [kV] | 120 (5min) | |
| Rated lightning impulse withstand voltage | to earth and between phases | [kV] | 190 (1,2/50µs) |
| across the isolating distance | [kV] | 220 (1,2/50µs) | |
| Rated frequency | [Hz] | 50 | |
| Rated continuous current | [A] | 630 | |
| Main busbars rated cotinuous current | [A] | 630 | |
| Rated short-time withstand current | [kA/1s] | up to 25 | |
| Rated peak withstand current | [kA] | up to 63 | |
| Withstand for internal arcing fault | [kA/1s] | up to 20 | |
| Protection degree | up to IP4X | ||
| Equipment: | ||
| Circuit breaker | Q1 | 3AH (SIEMENS); VD4/HD4 (ABB) |
| Earthing switch | Q3 | UW36 |
| Current transformer | T1 | various manufacturers |
| Voltage transformer | T2 | various manufacturers |
| Overvoltage limiter | F1 | various manufacturers |
| Weight | [kg] | 1380 |
| Note: We allow the possibility of arranging the bay configuration concerning its function and equipment (type/manufacturer) |
||
Sheet 2.2 - Feeder bay with switch disconnector
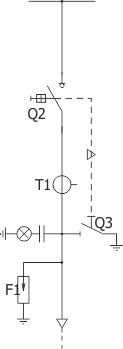
| Parameters: | |||
| Rated voltage | [kV] | 36 | |
| Rated power-frequency withstand voltage | to earth and between phases | [kV] | 85 (5min) / 95 (1min) |
| across the isolating distance | [kV] | 120 (5min) | |
| Rated lighting impulse withstand voltage | to earth and between phases | [kV] | 190 (1,2/50µs) |
| across the isolating distance | [kV] | 220 (1,2/50µs) | |
| Rated frequency | [Hz] | 50 | |
| Rated continuous current | [A] | 630 | |
| Main busbars rated cotinuous current | [A] | 630 | |
| Rated short-time withstand current | [kA/1s] | up to 25 | |
| Rated peak withstand current | [kA] | up to 63 | |
| Withstand for internal arcing fault | [kA/1s] | up to 20 | |
| Protection degree | up to IP4X | ||
| Equipment: | ||
| Switch disconnector | Q2 | NAL 36 (ABB) |
| Earthing switch | Q3 | UW36 |
| Current transformer | T1 | various manufacturers |
| Overvoltage limiter | F1 | various manufacturers |
| Weight | [kg] | 1150 |
| Note: We allow the possibility of arranging the bay configuration concerning its function and equipment (type/manufacturer) |
||
Sheet 2.3 - Bus coupler bay - cubicle with circuit breaker
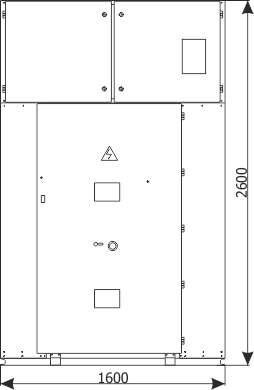
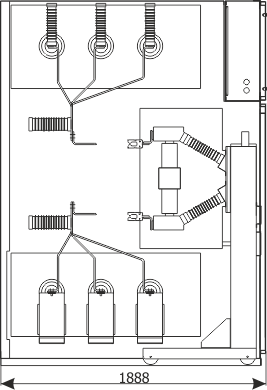
| Parameters: | |||
| Rated voltage | [kV] | 36 | |
| Rated power-frequency withstand voltage | to earth and between phases | [kV] | 85 (5min) / 95 (1min) |
| across the isolating distance | [kV] | 120 (5min) | |
| Rated lighting impulse withstand voltage | to earth and between phases | [kV] | 190 (1,2/50µs) |
| across the isolating distance | [kV] | 220 (1,2/50µs) | |
| Rated frequency | [Hz] | 50 | |
| Rated continuous current | [A] | 630 | |
| Main busbars rated cotinuous current | [A] | 630 | |
| Rated short-time withstand current | [kA/1s] | up to 25 | |
| Rated peak withstand current | [kA] | up to 63 | |
| Withstand for internal arcing fault | [kA/1s] | up to 20 | |
| Protection degree | up to IP4X | ||
| Equipment: | ||
| Circuit breaker | Q1 | 3AH (SIEMENS); VD4/HD4 (ABB) |
| Current transformer | T1 | various manufacturers |
| Weight | [kg] | 1300 |
| Notice: We allow the possibility of arranging the bay configuration concerning its function and equipment (type/manufacturer) |
||
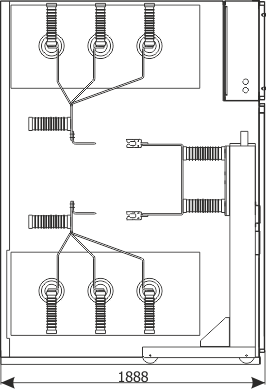
Sheet 2.4 - Bus coupler bay - cubicle with sectionalizer

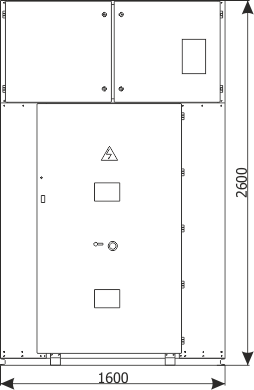
| Parameters: | |||
| Rated voltage | [kV] | 36 | |
| Rated power-frequency withstand voltage | to earth and between phases | [kV] | 85 (5min) / 95 (1min) |
| across the isolating distance | [kV] | 120 (5min) | |
| Rated lighting impulse withstand voltage | to earth and between phases | [kV] | 190 (1,2/50µs) |
| across the isolating distance | [kV] | 220 (1,2/50µs) | |
| Rated frequency | [Hz] | 50 | |
| Rated continuous current | [A] | 630 | |
| Main busbars rated cotinuous current | [A] | 630 | |
| Rated short-time withstand current | [kA/1s] | up to 25 | |
| Rated peak withstand current | [kA] | up to 63 | |
| Withstand for internal arcing fault | [kA/1s] | up to 20 | |
| Protection degree | up to IP4X | ||
| Equipment: | ||
| Sectionalizer | Q4 | made by ZPUE |
| Weight | [kg] | 1150 |
| Note: We allow the possibility of arranging the bay configuration concerning its function and equipment (type/manufacturer) |
||
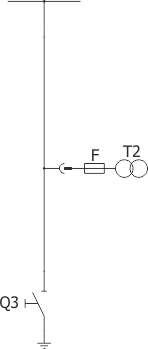
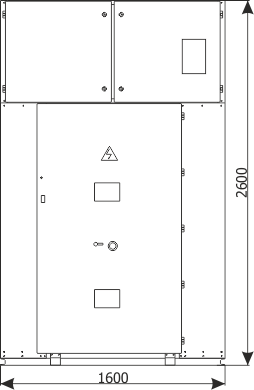
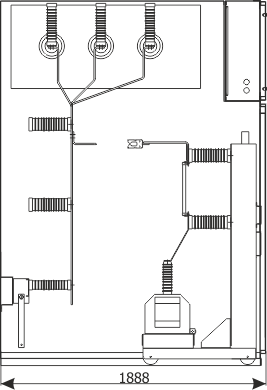
Sheet 2.5 - Metering bay
| Parameters: | |||
| Rated voltage | [kV] | 36 | |
| Rated power-frequency withstand voltage | to earth and between phases | [kV] | 85 (5min) / 95 (1min) |
| across the isolating distance | [kV] | 120 (5min) | |
| Rated lighting impulse withstand voltage | to earth and between phases | [kV] | 190 (1,2/50µs) |
| across the isolating distance | [kV] | 220 (1,2/50µs) | |
| Rated frequency | [Hz] | 50 | |
| Main busbars rated cotinuous current | [A] | 630 | |
| Rated short-time withstand current | [kA/1s] | up to 25 | |
| Rated peak withstand current | [kA] | up to 63 | |
| Withstand for internal arcing fault | [kA/1s] | up to 20 | |
| Protection degree | up to IP4X | ||
| Equipment: | ||
| Withdrawable module | withdrawable module with voltage transformers | |
| Earthing switch | Q3 | UW36 |
| Voltage transformer | T2 | various manufacturers |
| Weight | [kg] | 1100 |
| Note: We allow the possibility of arranging the bay configuration concerning its function and equipment (type/manufacturer) |
||
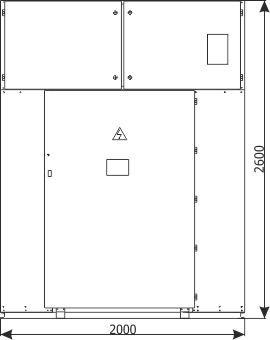
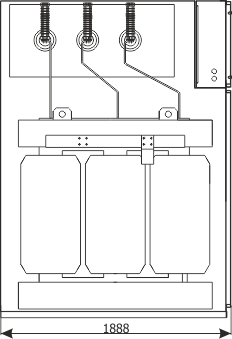
Sheet 2.6 - Auxiliary transformer bay
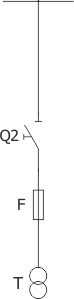
| Parameters: | |||
| Rated voltage | [kV] | 36 | |
| Rated power-frequency withstand voltage | to earth and between phases | [kV] | 85 (5min) / 95 (1min) |
| across the isolating distance | [kV] | 120 (5min) | |
| Rated lighting impulse withstand voltage | to earth and between phases | [kV] | 190 (1,2/50µs) |
| across the isolating distance | [kV] | 220 (1,2/50µs) | |
| Rated frequency | [Hz] | 50 | |
| Main busbars rated cotinuous current | [A] | 630 | |
| Rated short-time withstand current | [kA/1s] | up to 25 | |
| Rated peak withstand current | [kA] | up to 63 | |
| Withstand for internal arcing fault | [kA/1s] | up to 20 | |
| Protection degree | up to IP4X | ||
| Equipment: | ||
| Disconnector/Switch disconnector | Q2 | ON/NAL (ABB) |
| Transformer | T | up to 100 kVA; 35/0,4 kV |
| Weight | [kg] | 2070 |
| Note: We allow the possibility of arranging the bay configuration concerning its function and equipment (type/manufacturer) |
||